I am a Postdoc scientist at the CAMS-Oxford Institute, University of Oxford.
Prior to this, I obtained a DPhil degree at the Kennedy institute, University of Oxford, under the supervision of Prof. Tonia Vincent, Dr. Ngee Han Lim and Prof. Bartlomiej W. Papiez,
a MRes degree at the Hamlyn Center for Robotic Surgery, Imperial College London, under the supervision of Prof. Guang-Zhong Yang,
and a BEng degree at University of Liverpool, with my final year project supervised by Dr. Lin Jiang and my second year project supervised by Prof. Shusen Yang.
My current research interests are in AI for Biomedicine, including biomedical data analysis, surgical navigation and computational biology, with an emphasis on the computational models and machine learning approaches.
News
- : Honored to join the Editorial Board of PLOS Digital Health, Public Library of Science.
- : Honored to join the Editorial Board of Frontiers of Medicine / MedScience, Springer Nature.
- : Honored to be recognized as an Outstanding Reviewer at CVPR 2025.
- :
Surg_NavigOne journal paper accepted by IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters with the released.
- :
Biomed_AnalyOne journal paper accepted by Medical Image Analysis. - :
Biomed_AnalyOne journal paper accepted by IEEE Trans on Signal Processing. - : Oxford Life Science Alliance (OLSA) Annual Symposium 2024 is held on Thursday, 7th March 2024, at Oxford.
- :
Biomed_AnalyOne journal paper accepted by Medical Image Analysis with.
- :
Biomed_AnalyOne journal paper accepted by Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics. - :
Comput_BioOne journal paper accepted by Cell Research with the released.
- : A 20-min oral presentation entitled "Recursive Deformable Image Registration Network with Mutual Attention" is given at MIUA 2022 in Cambridge.
- :
Surg_NavigOne conference paper accepted by MICCAI 2022 with the released.
- :
Biomed_AnalyTwo conference papers accepted by MIUA 2022, one oral presentation and one poster session.
Selected Research Projects
a. Biomedical Data Analysis
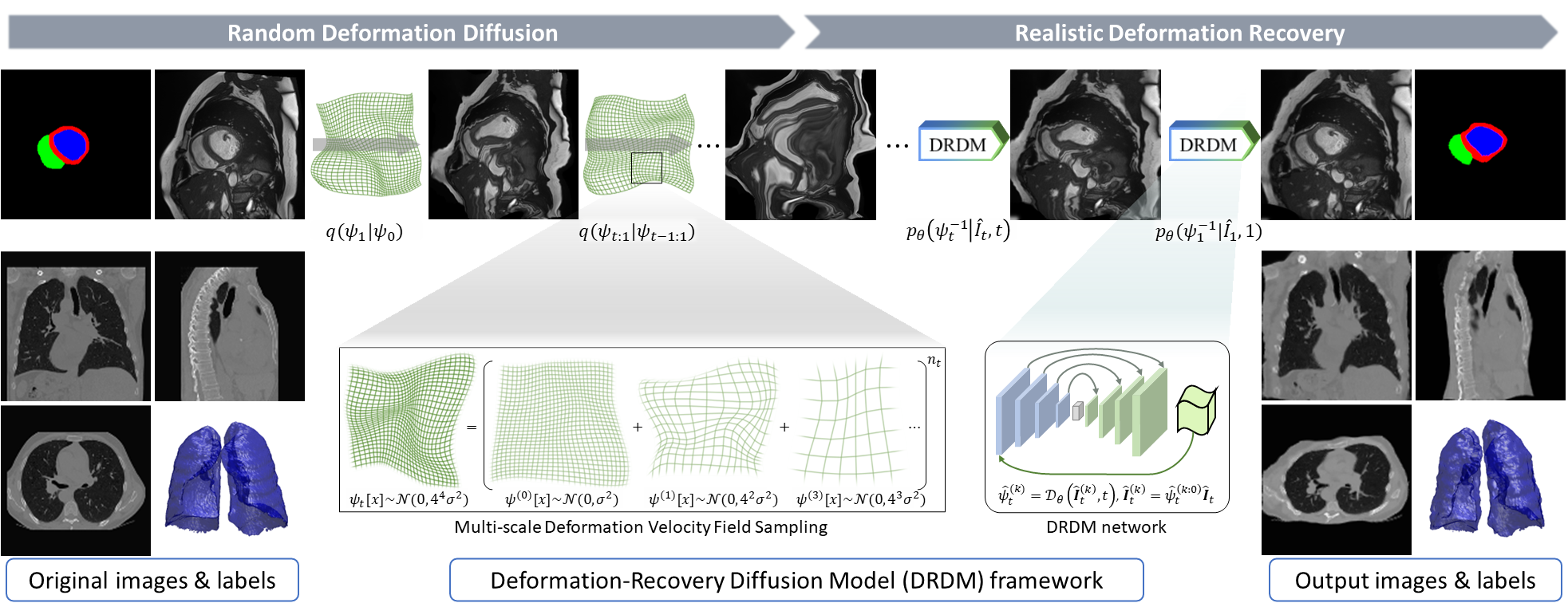
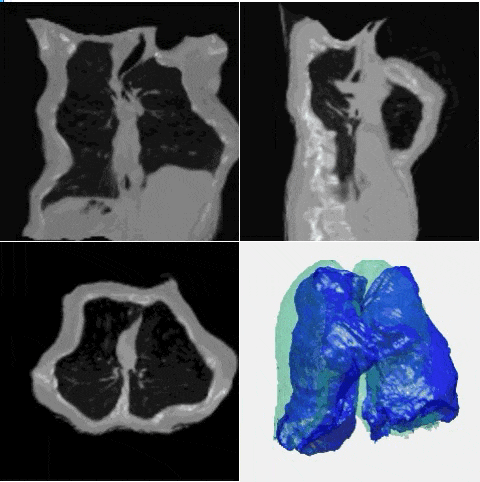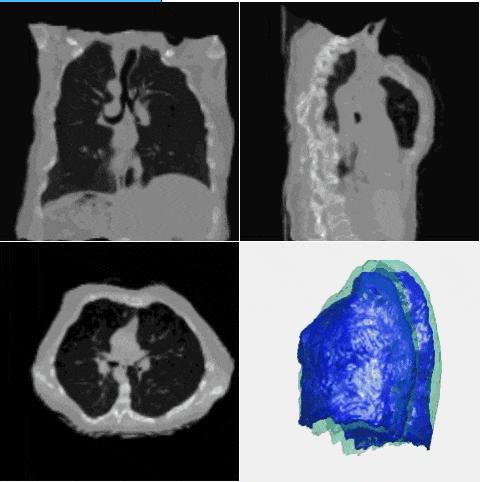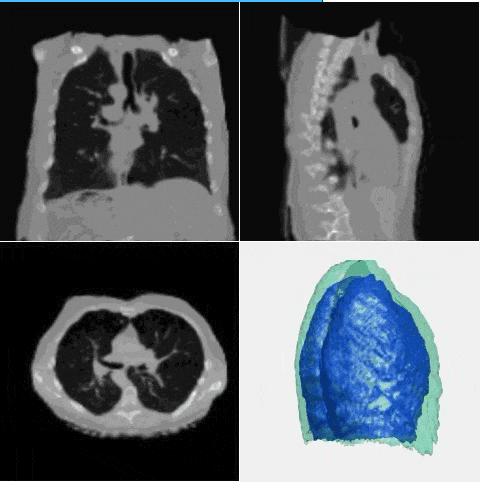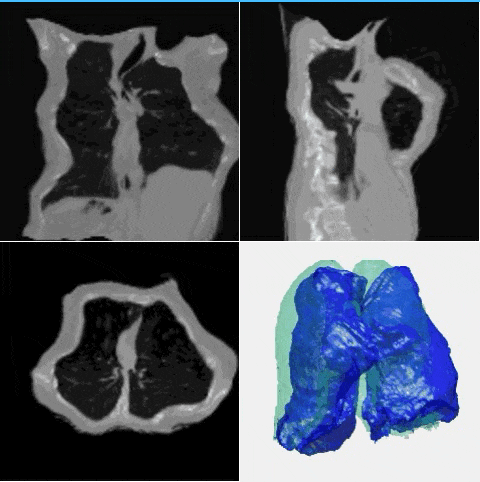
J. Q. Zheng†, Y. Mo†, Y. Sun, J. Li, F. Wu, Z. Wang, T. Vincent, B. W. Papiez
- This is the first study to explore diverse deformation generation for one specific image without an atlas image.
- - A novel diffusion model is proposed based on deformation diffusion and recovery.
- - The model generates diverse and realistic deformation for each instance image.
- - A random and reasonable deformation field sampling method is proposed for training.
- - The model enables and improves data augmentation in few-shot segmentation.
- - The model enables and improves data synthesis for registration model training.
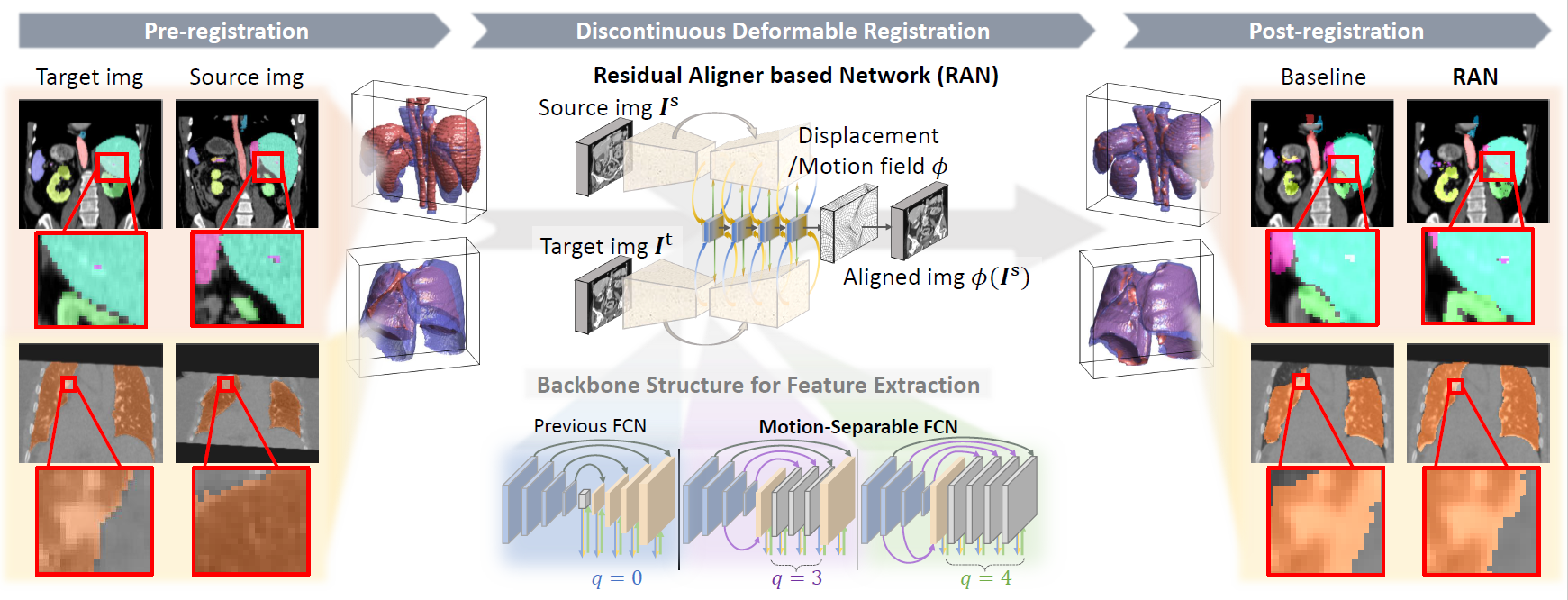
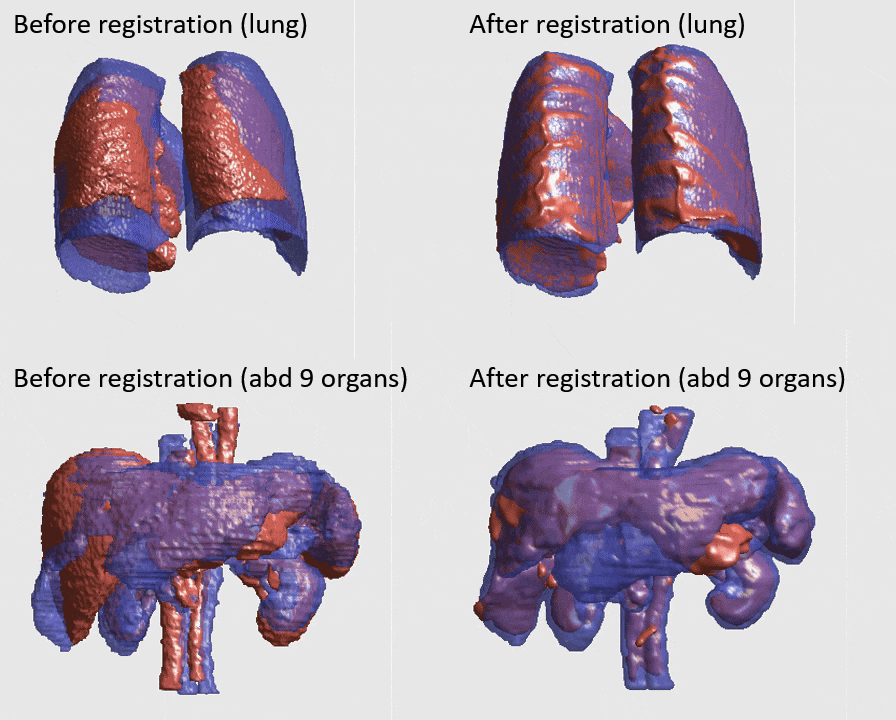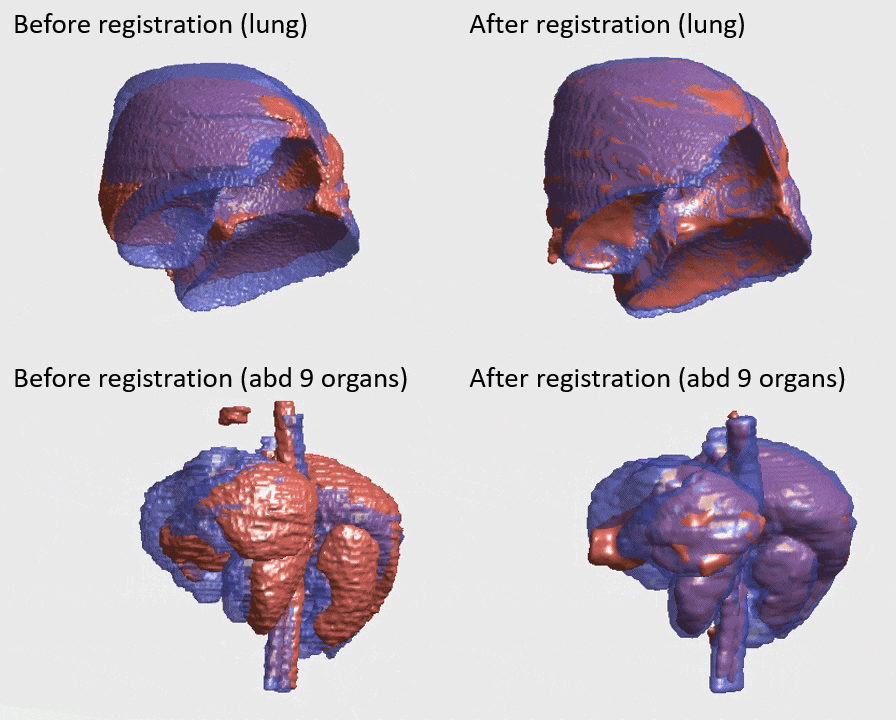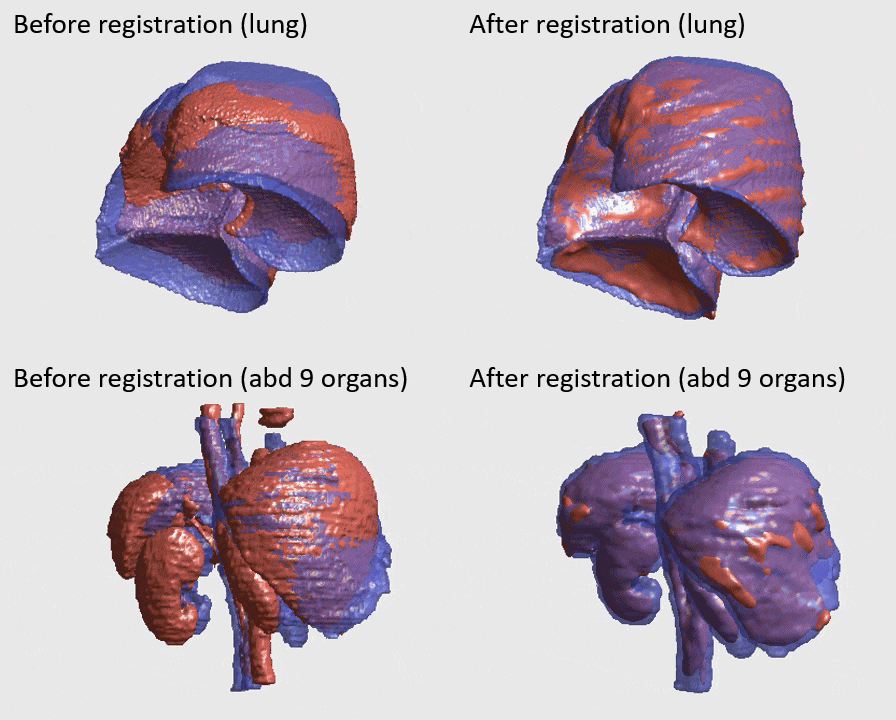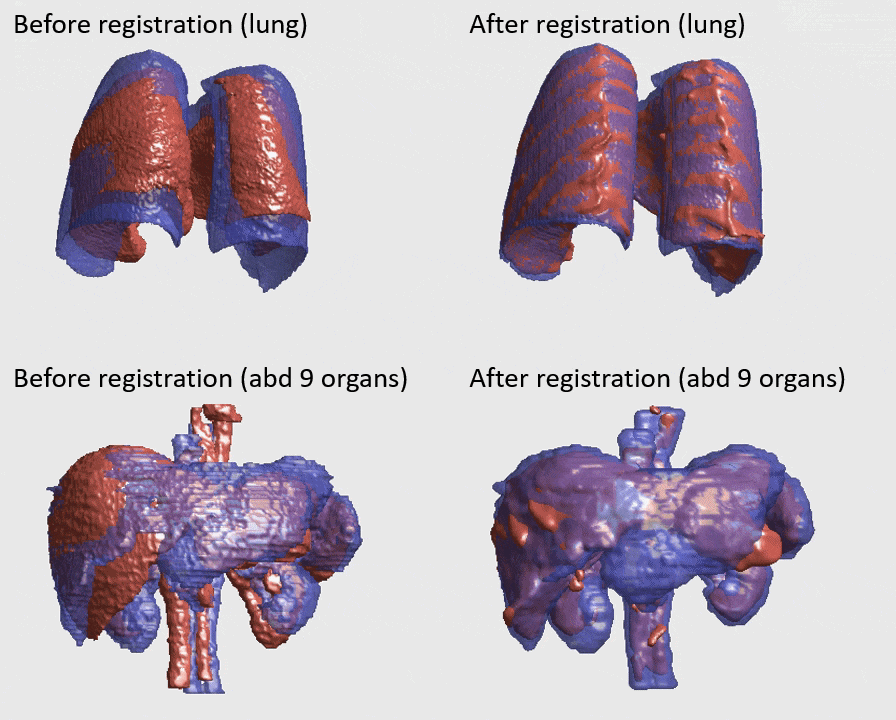
J. Q. Zheng, Z. Wang, B. Huang, N. H. Lim, B. W. Papiez
- This is the first quantitative investigation of deep learning methods for discontinuous deformable registration.
- - The proposed RAN obtains the state-of-the-art accuracy and better efficiency.
- - Motion separability quantifies upper limit of the predictable motions' difference.
- - Motion-Separable structure is used for a higher motion separability.
- - Multi-head mask is used to disentangle the motions of different organs.
- - Confidence weight is estimated to the weight and refine the predicted motions.
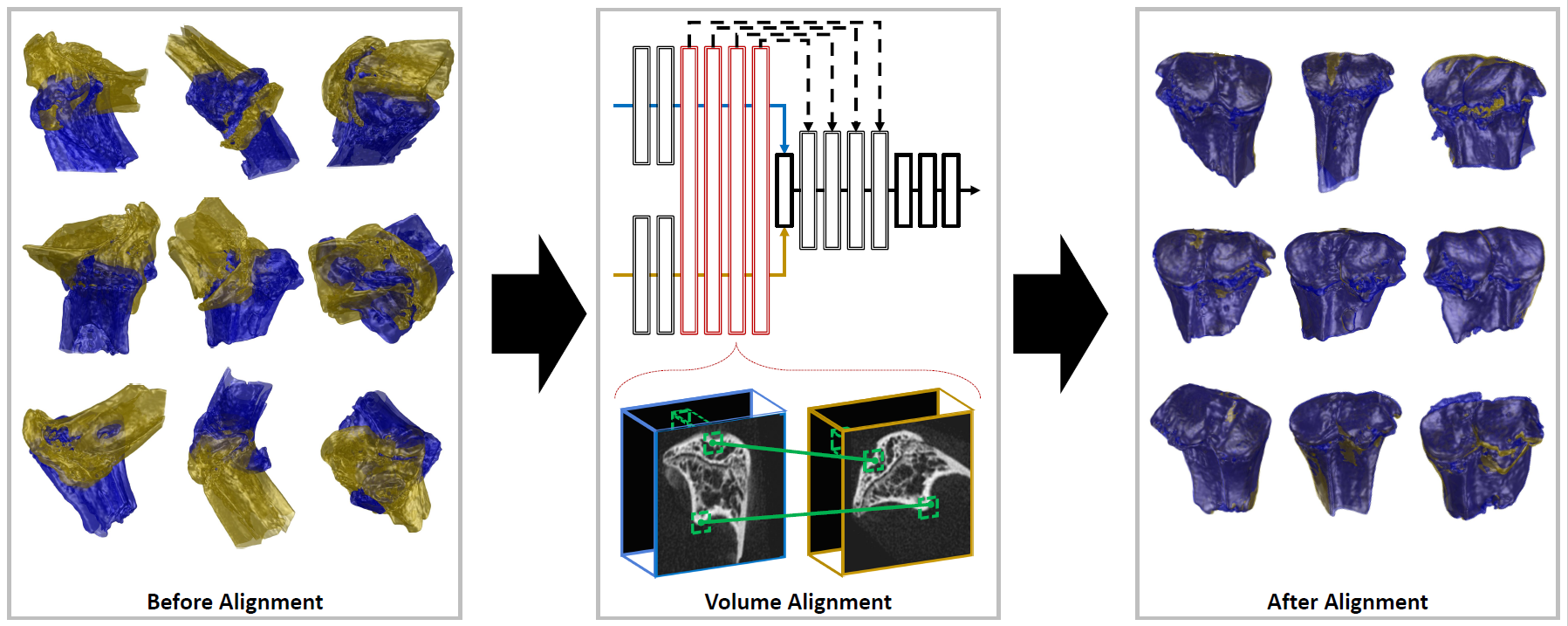
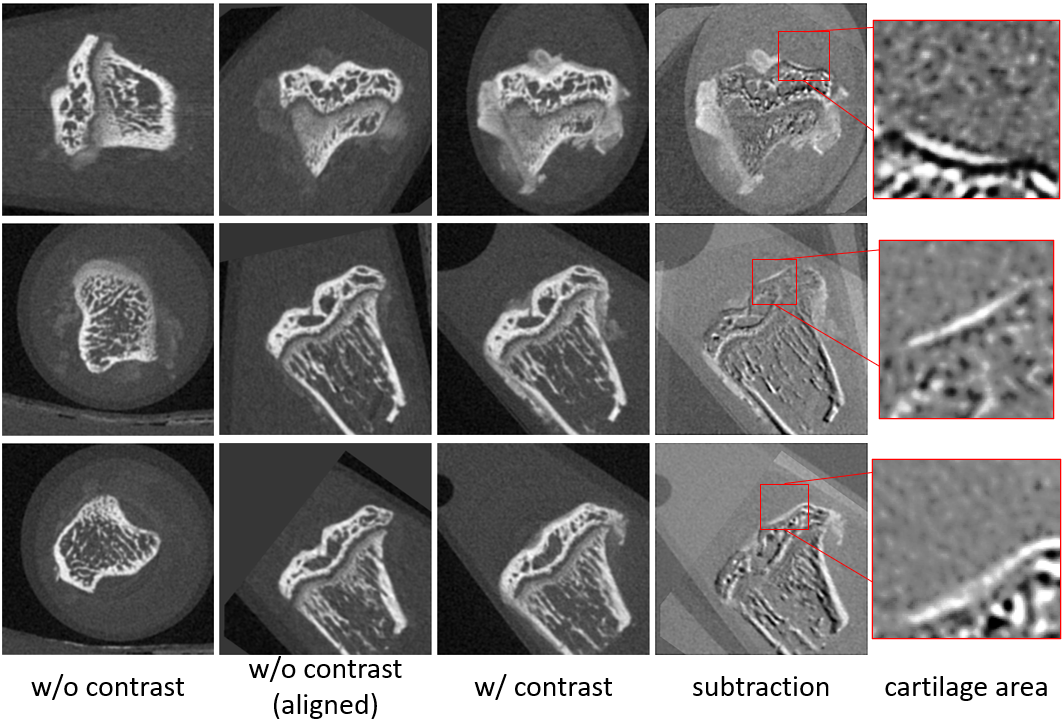
Accurate volume alignment of arbitrarily oriented tibiae based on a mutual attention network for osteoarthritis analysis
|

D-net: siamese based network for arbitrarily oriented volume alignment
|

J. Q. Zheng, N. H. Lim, B. W. Papiez
- It is the earliest work that applies the attention mechanism to image registration, enabling sub-voxel errors even from an arbitrary initial orientation.
- - Alignment of arbitrary oriented CT volumes allows extraction of contrasted cartilage.
- - Only proposed D-net achieved accurate alignment of arbitrary oriented volumes.
- - D-net extracts the common features and the spatial information via Siamese structure.
- - Mutual attention enhances long-range connection between two-branch D-net structure.
- - The alignment framework may be generalizable for multiple longitudinal studies.


ACNN: a Full Resolution DCNN for Medical Image Segmentation
X. Y. Zhou†, J. Q. Zheng†, P. Li, G. Z. Yang
- A pooling-free network structure is proposed to achieve full-resolution feature processing using a theoretically optimal dilation setting for a larger receptive field, which achieves a higher accuracy even with fewer parameters.
- - The left figure shows the receptive field with the dilation setting (1,2,5...) used for DeepLab.
- - The right figure shows the receptive field with the dilation setting (1,3,9...) used for our ACNN.
- - Our setting achieves larger receptive field with the same number of layers.
b. Surgical Navigation

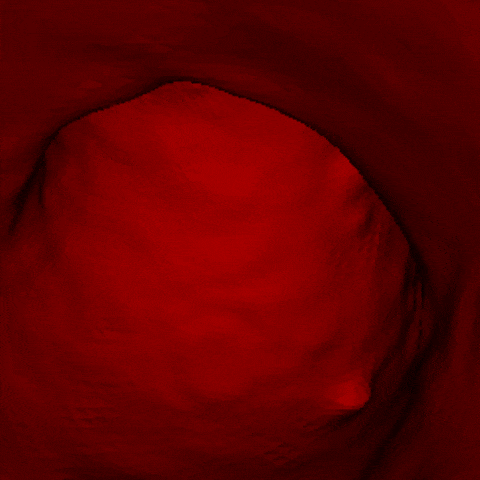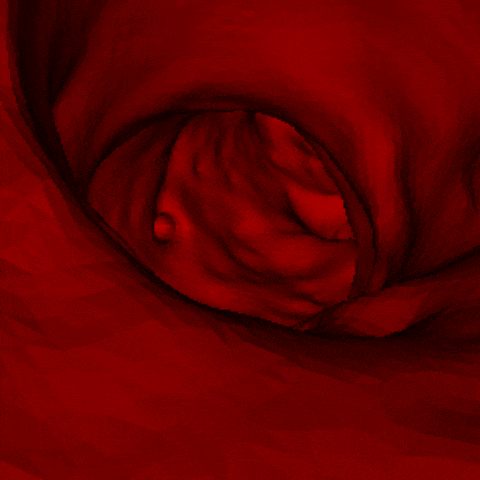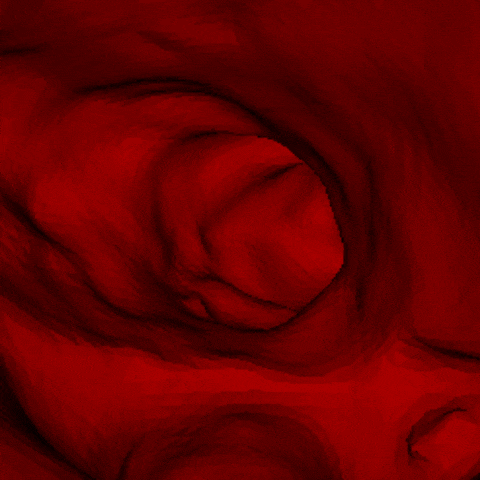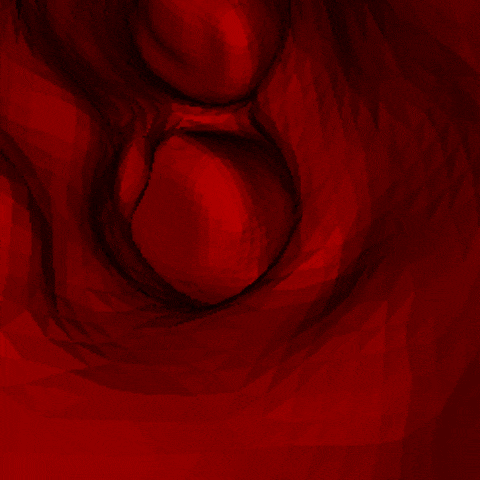
J. Q. Zheng, X. Y. Zhou, C. Riga, G. Z. Yang
- The first real-time framework of 3D intra-operative AAA skeleton instantiation from a single 2D AAA fluoroscopic image is proposed for 3D robotic path planning, achieving sub-pixel error in the clinical data.
- - Left: the 3D abdominal aortic center line recovered from one 2D X-ray image.
- - Right: how it looks like when a catheter moves along the recovered center line of aorta.
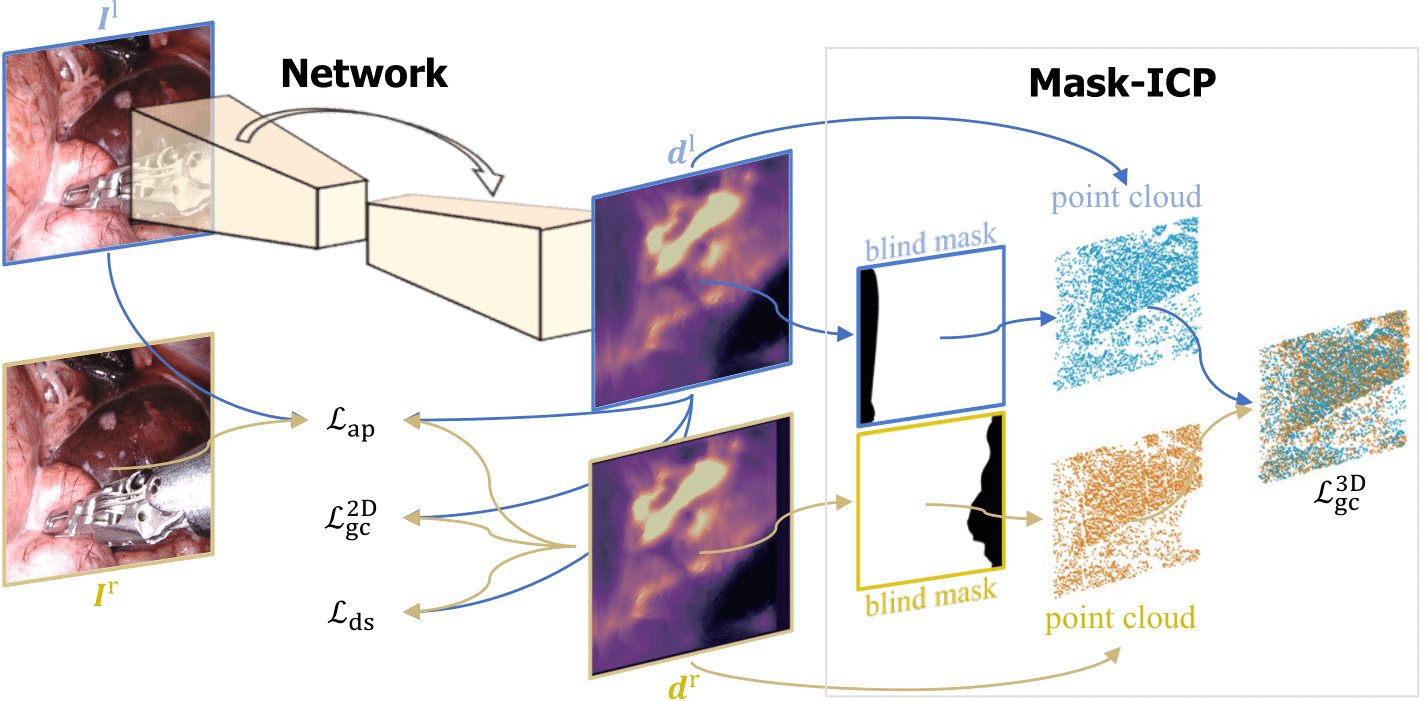
Self-Supervised Depth Estimation in Laparoscopic Image using 3D Geometric Consistency
B. Huang, J. Q. Zheng, A. Nguyen, C. Xu, I. Gkouzionis, K. Vyas, D. Tuch, S. Giannarou, D. S. Elson
- - Most recent depth estimation work focused on the left-right consistency in 2D and ignored valuable inherent 3D information on the object in real world coordinates, meaning that the left-right 3D geometric structural consistency is not fully utilized.
- - To overcome this limitation, we present M3Depth, a self-supervised depth estimator to leverage 3D geometric structural information hidden in stereo pairs while keeping monocular inference.
- - The method also removes the influence of border regions unseen in at least one of the stereo images via masking, to enhance the correspondences between left and right images in overlapping areas.
- - Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms previous self-supervised approaches on both a public dataset and a newly acquired dataset by a large margin, indicating a good generalization across different samples and laparoscopes.
c. Computational Biology and Bioinformatics
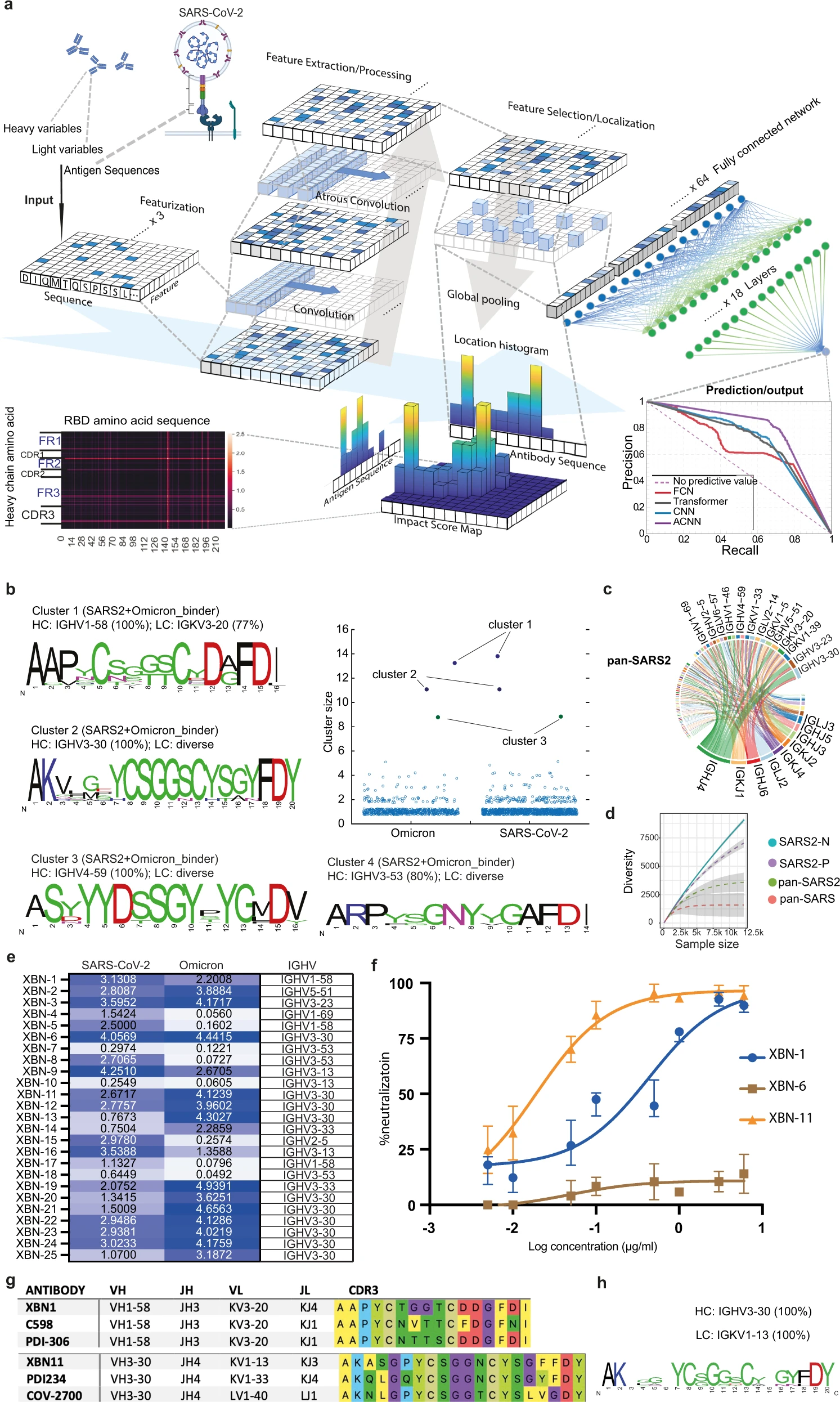
H. Lou†, J. Q. Zheng†, X. Fang, Z. Liang, M. Zhang, Y. Chen, C. Wang, and X. Cao.
- The first deep learning method is proposed for predicting cross-reactive antibodies, using ACNN structure for feature extraction.
- a. The features of the amino acid sequences of VH, VL and RBD sequences were extracted, localized and max-pooled to be concatenated together as input to the fully connected layers. The active features in the latent space were then processed by Multi-Layer Perceptron to predict the binding probability of antibody to multiple antigens. The impact score of VH, VL and RBD is calculated on the local histogram impact score map, representing how much weight is given to the specified amino acids on VH, VL (y axis) and RBD (x axis). Prediction results are evaluated by Precision-Recall curves of ACNN (Violet), Transformer (Gray), FCN (Red) and CNN (Blue).
- b. The HCDR3 sequences of the predicted SARS-CoV-2 and Omicron variant binders are clustered by using an 80% sequence similarity. Cluster size represents the number of BCR sequences in the cluster. For each expanded cluster, the HCDR3 sequences are visualized as a sequence logo plot, where y-axis represents the frequency of the individual amino acid at the corresponding position in x-axis. The frequency of the dominating VH gene is listed above the logo.
- c. Circos plot showing the frequency of antibodies encoded by the specified V region to J region pairing of the pan-SARS2 sequences.
- d. The diversity of the four groups of BCR repertoire is analyzed, which is linked to the sample number of each group.
- e. Binding of the predicted cross-reactive antibodies to RBD of SARS-CoV-2 and Omicron variants (left panel) was examined by ELISA. Representative OD reading is plotted as heatmap ranging from 0.05 to 5.0, and OD of 0.1 is used as cut-off value (n = 3 per group).
- f. The SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant (BA.1) pseudovirus neutralization curves of XBN-1, XBN-6 and XBN-11 mAbs were generated from luciferase readings at 8 dilutions (n = 3).
- g. HCDR3 sequences of the XBN-1 and XBN-11 are aligned with the most convergent anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from the published studies.
- h. The HCDR3 sequence frequency of the dominant cluster (encoded by IGHV3-30 and IGKV1-13) of the pan-SARS group is shown.
Talks
- “AI-assisted segmentation and thickness measurement of cartilage shape from CT scans contrasted with a type II collagen binding peptide containing di-iodotyrosine”, Cutting Edge Osteoarthritis Meeting, 2023, poster presentation.
- “Recursive Deformable Image Registration Network with Mutual Attention”, the 26th Annual Conference for Medical Image Understanding and Analysis, 2022, 20-minute oral presentation.
- “An AI model for aligning and extracting cartilage shape from CT scans contrasted with a type II collagen binding peptide containing di-iodotyrosine”, Cutting Edge Osteoarthritis Meeting, 2022, 3-minute talk & poster presentation.
- “D-Net: An AI model for aligning volumes, developed for cartilage segmentation from CT scans contrasted with a type II collagen binding peptide containing di-iodotyrosine”, British Society for Matrix Biology meeting, 2020, 3-minute talk presentation.
- “D-net: Siamese Based Network for Arbitrarily Oriented Volume Alignment”, International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, 2020, 3-minute talk & poster presentation.
- “Towards 3D Path Planning from a Single 2D Fluoroscopic Image for Fenestrated Endovascular Aortic Repair”, IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2019, 3-minute talk & poster presentation.
Academic Services
Editorial Board
- PLOS Digital Health, Public Library of Science
- Frontiers of Medicine / MedScience, Springer Nature
Co-organizer
- the 26th Annual Conference of the Chinese Life Scientist Society in the UK (promoted by CLSS-UK)
- the 28th-43th Oxford Life Science Association Monthly Seminar (former name: OCLSS Seminar, promoted via twitter and facebook)
Journal Reviewer
- Medical Image Analysis (MedIA), Elsevier
- Pattern Recognition (PR), Elsevier
- Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (AIIM), Elsevier
- Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine (CMPB), Elsevier
- International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV), Springer
- Journal of Imaging Informatics in Medicine / Journal of Digital Imaging (JDIM), Springer
- Frontiers of Medicine / MedScience, Springer Nature
- IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (TIP)
- IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT)
- IEEE Transactions on Robotics (T-RO)
- IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L)
- IEEE Signal Processing Letters (SPL)
- PLOS Digital Health, Public Library of Science (PLoS)
Conference Reviewer
- International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2021, Springer
- Annual Conference on Medical Image Understanding and Analysis (MIUA) 2022, Springer
- European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) 2022/2024, Springer
- IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2025
- IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) 2025
- IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) 2025
- IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2020/2025
- IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 2025
- UK-RAS Network Conference on Robotics and Autonomous Systems (UK-RAS) 2019
Thank Mr. Yi Ren for sharing the source code of the website template.
























